Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 School of Physics and Optoelectronics; State Key Laboratory of Luminescent Materials and Devices, Guangdong Engineering Technology Research and Development Center of Special Optical Fiber Materials and Devices, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Fiber Laser Materials and Applied Techniques, South China University of Technology, Guangzhou 510640, China
2 Research Institute of Future Technology, South China Normal University, Guangzhou 510006, China
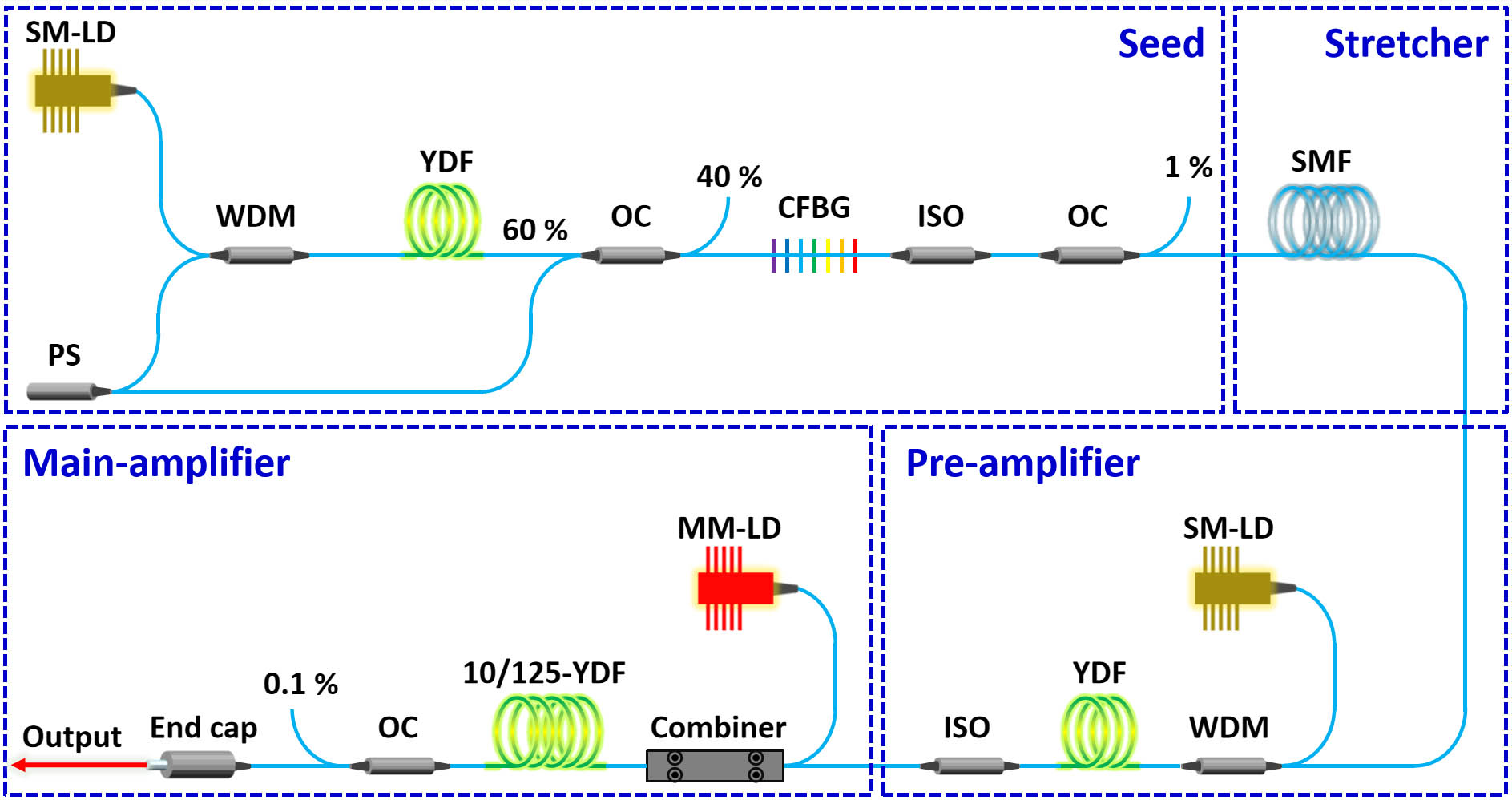
We report a high-stability ultrafast ultraviolet (UV) laser source at 352 nm by exploring an all-fiber, all-polarization-maintaining (all-PM), Yb-doped femtosecond fiber laser at 1060 nm. The output power, pulse width, and optical spectrum width of the fiber laser are 6 W, 244 fs, and 17.5 nm, respectively. The UV ultrashort pulses at a repetition rate of 28.9 MHz are generated by leveraging single-pass second-harmonic generation in a 1.3-mm-long BiB3O6 (BIBO) and sum frequency generation in a 5.1-mm-long BIBO. The maximum UV output power is 596 mW. The root mean square error of the output power of UV pulses is 0.54%. This laser, with promising stability, is expected to be a nice source for frontier applications in the UV wavelength window.
all-polarization-maintaining fiber ultrafast fiber laser UV laser Chinese Optics Letters
2024, 22(3): 031404
1 天津大学精密测试技术及仪器国家重点实验室,天津 300072
2 微纳制造实验室,天津 300072
工件的表面质量对零件可靠性、质量和使用寿命的影响至关重要。尽管各种基于计算机视觉的目标检测框架已经被广泛应用于工业表面缺陷检测场景,但由于面型的影响以及缺陷之间的混叠性,超精加工工件表面缺陷检测仍然具有挑战性。因此,提出了一种频率嵌入双分支参数预测网络来预测滤波参数,滤除掉型面信息从而使得缺陷特征更加显著。基于智能型面分析的预处理后,提出了一种基于级联区域神经网络感受野增强缺陷检测网络,将可变形卷积间隔地替换到高效网络的卷积模块中,有效地提高了主干网络特征提取的能力,然后重新选择特征图组成新的特征金字塔网络以提高效率,进一步提高网络性能。此外,还构建了具有滤波参数标注信息的滤波参数数据集UPP-CLS和具有缺陷类别及位置的缺陷检测数据集UPP-DET。模型在UPP-CLS上达到了85.36%的准确性,相较于现有网络提升3~5个百分点;在UPP-DET上达到了0.862的平均精度,相较于现有网络提升5.3%~7.8%。模型整体性能优于主流网络结构。源代码将在https://gitee.com/zihaodl/detect_app上开源。
超精密加工 计算机视觉 缺陷检测 型面分析 激光与光电子学进展
2023, 60(24): 2412006

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 South China University of Technology, School of Physics and Optoelectronics, Guangzhou, China
2 South China University of Technology, State Key Laboratory of Luminescent Materials, Guangzhou, China
3 South China University of Technology, Guangdong Engineering Technology Research and Development Center of Special Optical Fiber Materials and Devices, Guangzhou, China
4 South China University of Technology, Guangdong Provincial Key Laboratory of Fiber Laser Materials and Applied Techniques, Guangzhou, China
5 South China Normal University, Research Institute of Future Technology, Guangzhou, China
Laser processing with high-power ultrashort pulses, which promises high precision and efficiency, is an emerging new tool for material structuring. High repetition rate ultrafast laser highlighting with a higher degree of freedom in its burst mode is believed to be able to create micro/nanostructures with even more variety, which is promising for electrochemical applications. We employ a homemade high repetition rate ultrafast fiber laser for structuring metal nickel (Ni) and thus preparing electrocatalysts for hydrogen evolution reaction (HER) for the first time, we believe. Different processing parameters are designed to create three groups of samples with different micro/nanostructures. The various micro/nanostructures not only increase the surface area of the Ni electrode but also regulate local electric field and help discharge hydrogen bubbles, which offer more favorable conditions for HER. All groups of the laser-structured Ni exhibit enhanced electrocatalytic activity for HER in the alkaline solution. Electrochemical measurements demonstrate that the overpotential at 10 mA cm - 2 can be decreased as much as 182 mV compared with the overpotential of the untreated Ni (-457 mV versus RHE).
high repetition rate ultrafast laser burst mode operation nickel electrocatalyst hydrogen evolution reaction Advanced Photonics Nexus
2023, 2(5): 056009
长沙理工大学电气与信息工程学院, 长沙 410000
针对传统导航方式精度低、误差大等问题, 结合视觉导航设计了一种基于ArUco码的着陆标识。对机载相机采集的实时影像进行图像处理, 利用世界坐标系与像素坐标系的映射关系建立无人机位姿估计模型, 以特征点坐标解算得到当前无人机与着陆标识物之间的相对姿态估计值, 设计并融合误差模型进一步提高定位精确性。通过无人机室外实际应用实验证明, 设计的降落标志及新型识别算法大大提高了无人机自主降落的精准性, 能更好地满足在**无人机等高精度降落要求场合的应用。
无人机 视觉导航 识别算法 自主降落 UAV visual navigation recognition algorithm autonomous landing
1 华南理工大学物理与光电学院,广东 广州 510610
2 华南师范大学未来技术研究院,广东 广州 510006
多维(多模)激光是突破单模激光技术瓶颈的重要途径,有望推动多学科交叉与创新发展。不同于传统的单模激光,多维激光具有光场结构复杂、可调控参数多等特点,其性能调控面临诸多挑战。近年来,随着人工智能的兴起,机器学习等智能调控技术被广泛用于光学系统性能的优化,推动了智能光学及相关学科的快速发展,为多维激光的智能调控提供了新思路。从激光谐振腔内部和外部调控两方面,介绍了智能调控技术在激光调控领域中的研究进展,并展望了智能调控多维激光技术在光学微操控、激光微加工和空间光通信等领域中的应用前景。
激光光学 激光束整形 光场调控 机器学习 多维度 中国激光
2023, 50(11): 1101004
1 天津大学精密仪器与光电子工程学院光纤光学及光通信实验室, 天津 300072
2 天津光电集团有限公司, 天津 300384
报道了一种基于非线性光纤环形镜的工作在耗散孤子共振(DSR)区域的被动锁模掺铒光纤激光器,分别在反常和正常色散区获得了方波脉冲输出。在腔内净色散值约为-0.32ps 2的反常色散区,当泵浦功率为481.2mW时,获得了最大时域宽度为33ns、单脉冲能量约为12.4nJ的方波脉冲。通过在腔内插入一段7m长的色散补偿光纤,使激光器工作在腔内净色散值约为2.85ps 2的正常色散区,在同样的泵浦条件下,获得了最大时域宽度为34.3ns、单脉冲能量约为9.42nJ的方波脉冲。这表明在满足腔内参数平衡的条件下,DSR方波脉冲可同时在反常和正常色散区产生。另外,还研究了泵浦功率对方波脉冲的时域宽度和单脉冲能量的影响,结果表明,随着泵浦功率的增加,方波脉冲的时域宽度和单脉冲能量均呈线性变化。
激光器 光纤激光器 耗散孤子共振 方波脉冲 非线性光纤环形镜 色散管理 中国激光
2020, 47(12): 1201006

Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Deparment of Biomedical Engineering, The Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong SAR, China
2 The Hong Kong Polytechnic University Shenzhen Research Institute, Shenzhen 518000, China
3 CAS Key Laboratory of Molecular Imaging, Institute of Automation, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Beijing 100190, China
4 Key Laboratory for Quantum Optics, Shanghai Institute of Optics and Fine Mechanics, Chinese Academy of Sciences, Shanghai 201800, China
5 Currently at: Department of Bioengineering, University of Pennsylvania, Philadelphia, Pennsylvania 19104, USA
Edge enhancement is a fundamental and important topic in imaging and image processing, as perception of edge is one of the keys to identify and comprehend the contents of an image. Edge enhancement can be performed in many ways, through hardware or computation. Existing methods, however, have been limited in free space or clear media for optical applications; in scattering media such as biological tissue, light is multiple scattered, and information is scrambled to a form of seemingly random speckles. Although desired, it is challenging to accomplish edge enhancement in the presence of multiple scattering. In this work, we introduce an implementation of optical wavefront shaping to achieve efficient edge enhancement through scattering media by a two-step operation. The first step is to acquire a hologram after the scattering medium, where information of the edge region is accurately encoded, while that of the nonedge region is intentionally encoded with inadequate accuracy. The second step is to decode the edge information by time-reversing the scattered light. The capability is demonstrated experimentally, and, further, the performance, as measured by the edge enhancement index (EI) and enhancement-to-noise ratio (ENR), can be controlled easily through tuning the beam ratio. EI and ENR can be reinforced by and folds, respectively. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first demonstration that edge information of a spatial pattern can be extracted through strong turbidity, which can potentially enrich the comprehension of actual images obtained from a complex environment.
Photonics Research
2020, 8(6): 06000954
1 天津大学精密仪器与光电子工程学院光纤光学及光通信实验室, 天津 300072
2 天津光电集团有限公司, 天津 300384
报道了一种基于非线性光纤环形镜(NOLM)、工作在耗散孤子共振(DSR)区的长腔被动锁模掺镱光纤激光器,该激光器谐振腔的总长度约为1502 m,可以输出重复频率为133.18 kHz的高能量方波脉冲,且输出脉冲的宽度和单脉冲能量均随泵浦功率的增大而呈线性增大。当泵浦功率增大到414.47 mW时,输出的方波脉冲具有最大宽度(761.6 ns),同时单脉冲能量达到了最大值(60.2 nJ)。通过改变NOLM中单模光纤的长度,进一步研究了谐振腔长度对输出方波脉冲特性的影响,结果表明:谐振腔越长,所得DSR方波脉冲越宽,脉冲峰值功率越低。
激光器 耗散孤子共振 方波 被动锁模 光纤激光器 非线性光纤环形镜
Author Affiliations
Abstract
1 Department of Biomedical Engineering, Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Hong Kong, P. R. China
2 Shenzhen Research Institute,Hong Kong Polytechnic University, Shenzhen 518057, P. R. China
3 Britton Chance Center for Biomedical Photonics, Wuhan National Laboratory for Optoelectronics, Huazhong University of Science and Technology, Wuhan, Hubei 430074, P. R. China
Wavefront shaping (WFS) techniques have been used as a powerful tool to control light propagation in complex media, including multimode fibers. In this paper, we propose a new application of WFS for multimode fiber-based sensors. The use of a single multimode fiber alone, without any special fabrication, as a sensor based on the light intensity variations is not an easy task. The twist effect on multimode fiber is used as an example herein. Experimental results show that light intensity through the multimode fiber shows no direct relationship with the twist angle, but the correlation coe±cient (CC) of speckle patterns does. Moreover, if WFS is applied to transform the spatially seemingly random light pattern at the exit of the multimode fiber into an optical focus. The focal pattern correlation and intensity both can serve to gauge the twist angle, with doubled measurement range and allowance of using a fast point detector to provide the feedback. With further development, WFS may find potentials to facilitate the development of multimode fiber-based sensors in a variety of scenarios.
Multimode fiber wavefront shaping scattering media fiber sensor optical focusing Journal of Innovative Optical Health Sciences
2019, 12(4): 1942007





